Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Singapore is a condition that arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel—a narrow passageway of ligament and bones at the base of the hand—houses the median nerve and tendons. When this tunnel narrows due to swelling or other reasons, it can pinch the nerve, leading to symptoms that affect hand and wrist function. At Apex sports clinic we provide carpal tunnel treatment Singapore with best surgeon in Singapore.
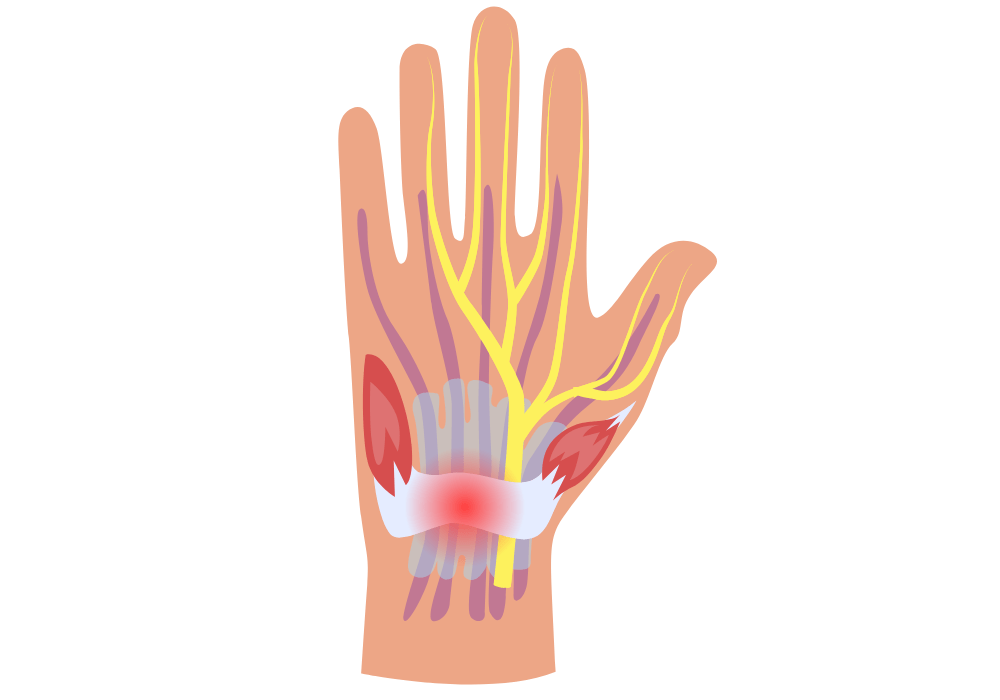
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that arises when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist.
Athletes involved in sports requiring repetitive wrist and hand motions, such as tennis, squash, and weightlifting, are at a higher risk. These repetitive actions can cause inflammation and swelling in the tendons, narrowing the carpal tunnel space.
Direct injury to the wrist, such as fractures or sprains, can cause swelling and pressure on the median nerve, leading to CTS.
Overuse of the wrist through intensive training sessions without adequate rest can strain the wrist tendons and ligaments, contributing to CTS.
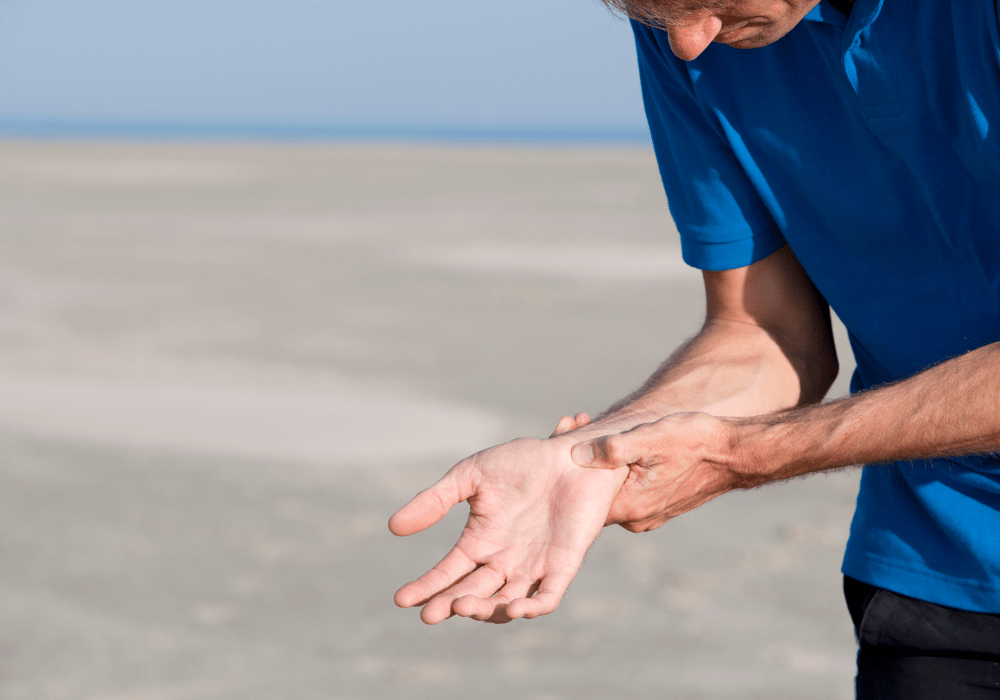

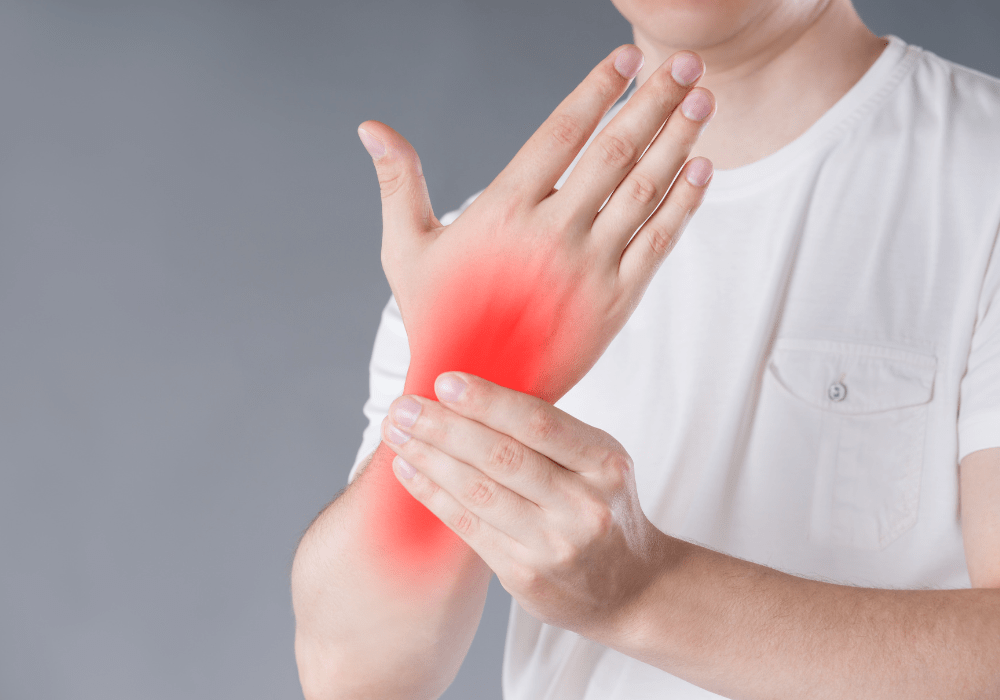

Recognizing the symptoms of CTS early can help in effective management and treatment.
A frequent tingling or numb sensation in the fingers (especially the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers) that can extend up the forearm.
Pain in the wrist, palm, or forearm, which may intensify during activities that involve gripping or pinching.
Weakness in the hand and difficulty performing fine motor tasks, such as gripping a racquet or lifting weights.
A burning sensation in the hand and wrist, often worsening at night or after prolonged use of the hand.
For athletes and individuals whose symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) do not improve with non-surgical treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. The goal of surgery is to relieve pressure on the median nerve by cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel.
Endoscopic Surgery
Endoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure designed to reduce recovery time and minimize scarring. This technique uses a small camera, called an endoscope, to guide the surgeon during the procedure.
Procedure Steps:
The surgeon makes one or two small incisions (about 1 centimeter) in the wrist and sometimes the palm. An endoscope, which is a thin tube with a camera and light at the end, is inserted through the incision. This device allows the surgeon to see inside the carpal tunnel without making a large incision. Using small, specialized instruments inserted through the endoscope, the surgeon cuts the transverse carpal ligament. This ligament forms the roof of the carpal tunnel and is the structure compressing the median nerve. Once the ligament is cut, the instruments and endoscope are removed, and the small incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips. The wrist is bandaged to protect the incisions and provide support during the initial healing phase.
Benefits:
– Smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain and scarring.
– Quicker recovery time compared to open surgery.
– Lower risk of infection and other complications.
Open Surgery
Open surgery is the traditional method for treating CTS and involves a larger incision to provide direct access to the carpal tunnel. This approach may be preferred for patients with more severe symptoms or when endoscopic surgery is not feasible.
Procedure Steps:
The surgeon makes a larger incision, usually about 2 inches long, along the palm of the hand, extending from the wrist. The skin and tissue layers are carefully separated to expose the carpal tunnel and the transverse carpal ligament. The surgeon cuts the transverse carpal ligament to release pressure on the median nerve. This may also involve removing any scar tissue or other abnormalities contributing to the compression. The incision is closed with sutures. The surgeon may also use adhesive strips to hold the skin edges together. The wrist and hand are bandaged to protect the wound and provide support during healing.
Benefits:
– Direct visualization of the carpal tunnel and structures, allowing for more precise treatment.
– Effective for severe cases where more extensive repair is needed.
– Potentially better outcomes in complex cases with significant structural issues.
Recovery Time
For Endoscopic Surgery – Patients can often return to light activities within a few days to weeks, with full recovery typically taking around 3-6 weeks.
For Open Surgery – Recovery might take longer, with patients resuming light activities in 4-6 weeks and full recovery in 6-12 weeks.
Rehabilitation:
Post-surgery, patients may need to wear a wrist splint to immobilize the area and facilitate healing.
A structured physical therapy program helps restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Exercises will be tailored to the patient’s needs and the specific demands of their sport. Pain relief is managed through prescribed medications, gradually reducing as healing progresses.
– Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor healing progress and ensure there are no complications.
– Adjustments to rehabilitation exercises and activity levels based on the patient’s recovery stage.
Key Takeaway
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can significantly impact an athlete’s performance and daily activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for effective management and recovery. Early diagnosis and intervention, whether through non-surgical or surgical means, can help athletes return to their peak performance levels. If you’re experiencing symptoms of CTS, don’t delay seeking professional medical advice.
Visit our sports clinic for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. With the right care and rehabilitation, you can overcome CTS and get back to doing what you love.
Elevate your performance with Apex Sports Clinic! Schedule an appointment today for personalized, expert care in optimizing your athletic potential.


