Are knee pains throwing off your game? Osgood-Schlatter disease, a common but often misunderstood condition that can put a damper on your sports adventures. It’s like a secret enemy lurking around your knees, causing discomfort and frustration, but fear not—we’re here to shed some light on this mysterious enemy!
Osgood-Schlatter disease, a prevalent condition among active adolescents, manifests as inflammation of the patellar tendon insertion at the tibial tuberosity. Occurring during periods of rapid growth, it commonly affects athletes engaged in high-impact sports.
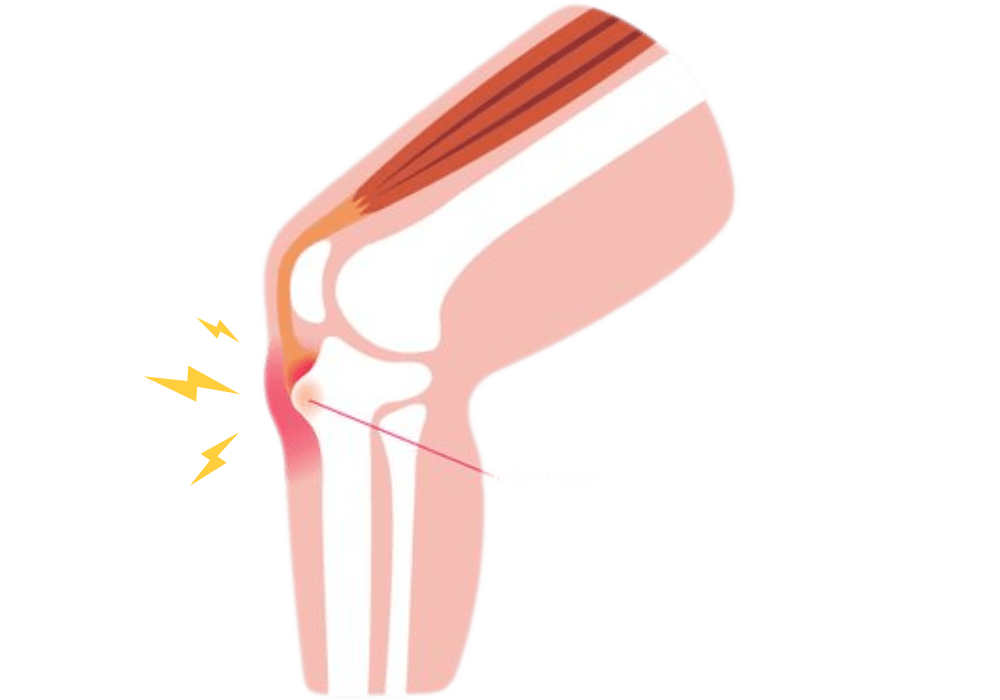
Are knee pains throwing off your game? Osgood-Schlatter disease, a common but often misunderstood condition that can put a damper on your sports adventures.
1. Excessive running, jumping, or kicking strains the knee, leading to irritation at the tibial tuberosity.
2. Rapid bone growth during adolescence can outpace muscle development, increasing tension on the patellar tendon.
3. Weak or tight quadriceps and hamstrings disrupt knee biomechanics, adding strain to the tibial tuberosity.
4. High-impact sports like basketball or soccer, with frequent jumping and cutting, heighten the risk of Osgood-Schlatter due to knee stress.

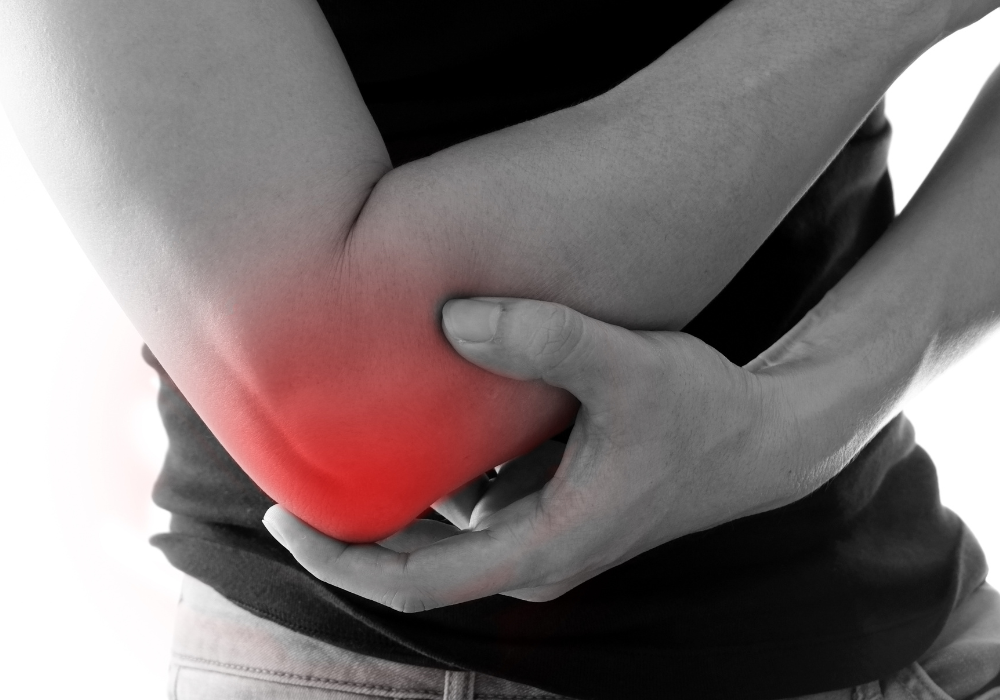

1. Persistent discomfort during knee movement, ranging from mild to severe.
2. Swelling and tenderness around the tibial tuberosity, especially when touched or pressed.
3. Knee stiffness upon waking or after rest, which typically eases with movement.
4. Prominent swelling below the kneecap, indicative of bony growth at the tibial tuberosity.
5. Decreased range of motion in the affected knee, making bending or straightening difficult.
Tibial Tubercle Osteotomy
During a tibial tubercle osteotomy, the surgeon makes an incision over the tibial tuberosity, the bony prominence below the kneecap where the patellar tendon attaches. Then, a carefully planned cut (osteotomy) is made in the tibial tubercle. This cut allows the surgeon to realign or remove a portion of the tuberosity to reduce tension on the patellar tendon. The realignment aims to restore proper biomechanics of the knee joint and alleviate symptoms associated with Osgood-Schlatter disease.
Benefits:
Considerations:
Recovery Time:
Following surgery, patients may require a period of immobilization or limited weight-bearing to allow the surgical site to heal properly. This phase typically lasts for a few weeks, during which physical therapy may be initiated to promote joint mobility and prevent stiffness.
Following surgical intervention, meticulous post-operative care includes:
Proper physical therapy programs aimed at restoring function and mobility.
Administration of prescribed medications and utilization of ice therapy for comfort.
Regular follow-up appointments to assess healing progress and address any complications.
Navigating Osgood-Schlatter disease necessitates a multifaceted approach, integrating both non-surgical and surgical modalities as warranted. With diligent management and expert guidance, individuals afflicted by this condition can achieve optimal recovery and resume their athletic endeavors with confidence.
Elevate your performance with Apex Sports Clinic! Schedule an appointment today for personalized, expert care in optimizing your athletic potential.


