Labral Tears
Labral Tear is a common struggle, but fear not!
Labral Tears
A labral tear is an injury to the labrum, a crucial ring of fibrocartilage that surrounds the hip joint’s socket, known as the acetabulum. The labrum plays a vital role in maintaining hip stability by deepening the socket, providing a more secure fit for the femoral head, which is the ball of the hip joint. This enhanced fit is essential for the stability and range of motion of the hip. Additionally, the labrum acts as a cushion, distributing the load across the hip joint to reduce stress on the cartilage. It also helps maintain a tight seal around the joint, crucial for proper lubrication and joint function.

Labral Tears
A labral tear is an injury to the labrum, a crucial ring of fibrocartilage that surrounds the hip joint's socket, known as the acetabulum
When the labrum is torn, its ability to stabilise the hip is compromised, leading to several potential issues. One major consequence is hip instability. Without the labrum stabilising effect, the femoral head may move excessively within the socket, increasing the risk of dislocation or partial dislocation (subluxation). This instability can significantly affect the hip’s functionality.
In addition, individuals with a labral tear often report clicking, catching, or locking sensations in the hip joint, especially during movement. These sensations are due to the disrupted function of the labrum and can further hinder normal hip use. Inflammation and swelling in the hip joint are common, exacerbating pain and mobility issues.
Let's’ explore the causes:
Sudden, Forceful Movements:
Many high-intensity sports involve rapid and forceful movements that place excessive strain on the hip joint. Activities such as tackling in football or rugby, powerful kicks in martial arts, and abrupt pivots in basketball or soccer can lead to labral tears due to the high demands placed on the hip’s stability and range of motion.
Repetitive Stress:
Sports that require repetitive actions, such as running, jumping, or twisting, can gradually wear down the labrum over time. This continuous stress can create small tears that eventually lead to significant damage. Endurance sports like long-distance running or cycling can also contribute to cumulative stress on the hip joint, increasing the risk of a tear.
Rapid Direction Changes:
Sports involving frequent and quick changes in direction, such as soccer, hockey, and basketball, can place a tremendous load on the hip joint. The sudden shifts in movement can cause the labrum to tear, especially if the joint is already under strain from previous activity.
High-Impact Collisions:
Contact sports are particularly risky for labral tears due to the potential for high-impact collisions. In football and rugby, players often experience direct hits to the hip area, which can cause immediate damage to the labrum. Similarly, in hockey, body checks and falls onto the hard ice surface increase the risk of injury.
Jumping and Landing:
Sports that involve significant jumping and landing, such as basketball, volleyball, and gymnastics, can cause labral tears. The impact forces generated during landing can transmit through the hip joint, creating stress that may lead to tearing of the labrum.
Overuse Injuries:
Athletes who train intensely and frequently without adequate rest may develop overuse injuries. Continuous overloading of the hip joint without proper recovery can weaken the labrum and surrounding structures, making it more susceptible to tearing.

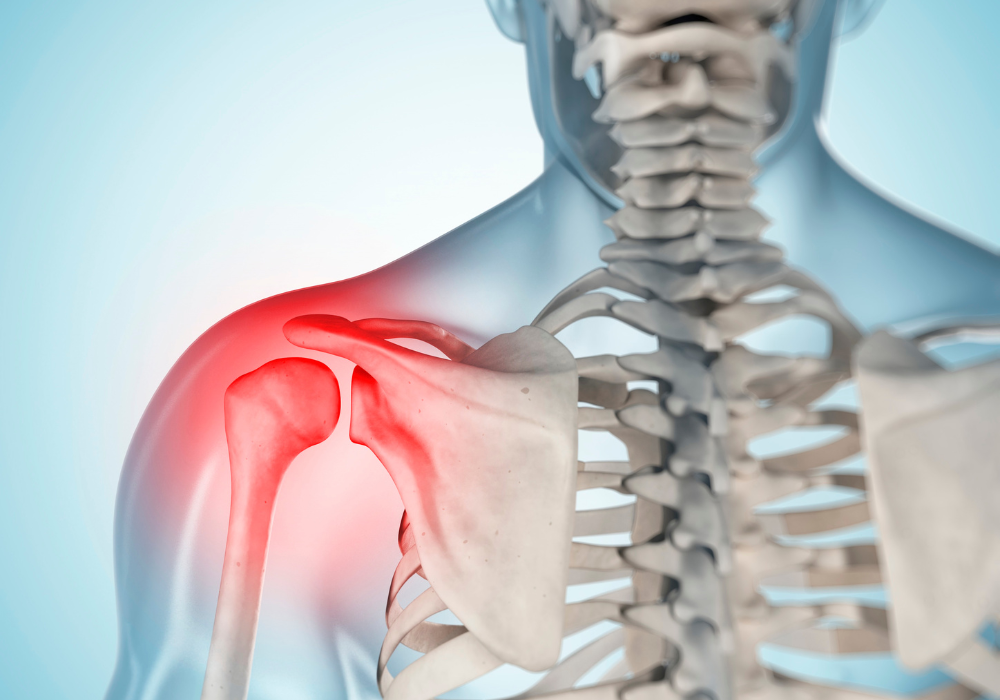

What are the Symptoms?
Severe Pain:
Individuals with a labral tear often experience intense pain in the hip or groyne area. This pain can be sharp and sudden, particularly during movements involving hip rotation or flexion. The discomfort may worsen with prolonged sitting, standing, or any activities that involve significant hip movement, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs. Nighttime pain can also be prevalent, affecting sleep quality and overall comfort.
Visible Deformity:
In cases where the labral tear leads to a hip dislocation, the affected leg may appear noticeably shorter than the other. The hip joint might look visibly out of place, with the thigh turned inward or outward in an abnormal position. Such deformities are often accompanied by significant swelling and may be easily noticeable even without a medical examination.
Limited Mobility:
A labral tear can severely restrict the hip’s range of motion, making it difficult or impossible to move the hip or leg normally. Simple activities like bending, sitting down, standing up, or even walking may become challenging and painful. Patients might experience a feeling of stiffness or locking in the hip joint, preventing smooth and fluid movements.
Swelling and Bruising:
The trauma associated with a labral tear or hip dislocation can lead to considerable swelling around the hip joint. This swelling is often accompanied by visible bruising. The inflammation may cause the hip area to feel warm and tender to the touch, contributing to overall discomfort and pain.
Swelling can exacerbate the pain and further restrict mobility, complicating daily activities and movements.
What are the Treatments?
Surgical Treatments:
Arthroscopic Surgery:
Minimally Invasive Procedure:
Arthroscopic surgery is a less invasive approach compared to traditional open surgery. It involves making small incisions through which a tiny camera, called an arthroscope, and specialised surgical instruments are inserted. This method minimises tissue damage and promotes faster recovery.
STEP 1 – Visualization of the Joint:
The arthroscope provides a clear, magnified view of the inside of the hip or shoulder joint on a monitor. This visualisation allows the surgeon to accurately identify and assess the extent of the labral tear.
STEP 2 – Repair or Removal of the Torn Labrum:
Labral Repair: If the labral tear is suitable for repair, the surgeon uses sutures or anchors to reattach the torn labrum to the bone. This is often the preferred method as it preserves the labrum’s function and promotes joint stability.
Labral Debridement: In cases where the tear is small or the labrum is too damaged to repair, the surgeon may opt to trim or remove the torn part of the labrum. This procedure, known as debridement, helps alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Open Surgery:
For More Extensive Tears:
Open surgery is typically reserved for more severe labral tears or when arthroscopic methods are not sufficient to address the damage. This might include cases with extensive labral damage or associated structural abnormalities. Open surgery involves making a larger incision to provide direct access to the shoulder joint. This allows the surgeon to perform a more comprehensive repair or reconstruction. The larger incision allows the surgeon to visualise the entire joint and address not only the labral tear but also any other issues that might be present, such as bone spurs, cartilage damage, or loose bodies within the joint.
Open surgery may be necessary for complex repairs that require precise manipulation and placement of surgical instruments. It can also be advantageous in cases where a more robust repair is needed to ensure long-term joint stability.
Post-Surgical Management
Rehabilitation:
Initial Rest:
Immediately following surgery, patients are typically advised to rest and avoid putting weight on the affected joint. This period allows the repaired labrum and surrounding tissues to begin healing without undue stress. Depending on the specific procedure and individual patient needs a sling might be used to immobilise the shoulder, respectively.
Gradual Increase in Activity:
After the initial rest period, a carefully structured rehabilitation program is crucial. This program begins with gentle, controlled movements to prevent stiffness and promote blood flow to the healing tissues. Activities are gradually increased in intensity and complexity, guided by the patient’s progress and pain levels.
Physical Therapy:
Range of Motion Exercises:
Early stages of physical therapy focus on restoring the joint’s range of motion. These exercises are designed to gently stretch and mobilise the joint without causing strain on the repaired labrum.
Strengthening Exercises:
As healing progresses, strengthening exercises are introduced to rebuild muscle mass and improve the stability of the joint. These exercises target the muscles surrounding the shoulder to enhance support and reduce the risk of re-injury.
Stability and Balance Training:
Stability exercises help improve the coordination and balance of the joint. This training is particularly important for athletes and individuals aiming to return to high-level physical activities. It involves exercises that challenge the joint’s stability in controlled environments, gradually progressing to more dynamic and unpredictable scenarios.
What is the Recovery Time?
The recovery timeline can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the severity of the labral tear, the type of surgical procedure performed, and the patient’s overall health and compliance with the rehabilitation program. On average, full recovery might take several months.
Initial Weeks:
During the first few weeks post-surgery, the focus is on minimising pain and swelling while protecting the repair. Patients typically experience gradual improvements in pain and mobility.
Intermediate Phase (6-12 Weeks):
Around the 6 to 12-week mark, most patients can expect to see significant improvements in joint function. Physical therapy intensifies, with more challenging exercises introduced to enhance strength and stability.
Long-Term Recovery (3-6 Months and Beyond):
Full recovery can extend to six months or more. During this phase, patients continue to work on advanced strengthening and functional exercises, aiming to return to pre-injury levels of activity. For athletes, this may include sport-specific drills and conditioning.
Throughout the recovery process, close communication with healthcare providers is essential to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the rehabilitation plan. Regular follow-up appointments help ensure that the joint is healing correctly and that the patient is on track to regain full function. Patience and adherence to the prescribed rehabilitation protocol are critical for a successful outcome.
Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances.
For personalised advice and treatment, please visit our clinic or contact our specialists.
Schedule An Appointment
Elevate your performance with Apex Sports Clinic! Schedule an appointment today for personalized, expert care in optimizing your athletic potential.


APEX SPORTS CLINIC
Search Here
Book An Appointment
Quick Links
Contact us
- Email Address
- admin@apexsportsclinic.sg
- Address
- #18-12, Royal Square Medical Center,101 Irrawaddy Road, Novena, Singapore 329565
- Phone
- +6587745468
- Address
- #03-03/04, i12 Katong, 112 East Coast Road, Singapore 428802
- Phone
- +6583219004
APEX SPORTS CLINIC
Search Here
Book An Appointment
Quick Links
Contact us
- Address
- #18-12, Royal Square Medical Center,101 Irrawaddy Road, Novena, Singapore 329565
- +6587745468
- Address
- #03-03/04, i12 Katong, 112 East Coast Road, Singapore 428802
- +6583219004
- Email Address
- admin@apexsportsclinic.sg

APEX SPORTS CLINIC
Quick Links
Search Here
Book An Appointment
Contact Us
- Email Address
- admin@apexsportsclinic.sg
- Address
- #18-12, Royal Square Medical Center,101 Irrawaddy Road, Novena, Singapore 329565
- Phone
- +6587745468
- Address
- #03-03/04, i12 Katong, 112 East Coast Road, Singapore 428802
- Phone
- +6583219004